If you have installed the latest version of RedHat based Linux and trying to run the “yum” command, you may get the “yum command not found error“. But why?? Because yum is obsolete now, “dnf” is the next-generation software package manager in Fedora, CentOS, AlmaLinux, and Rocky Linux.
This article will help you to solve all the below mentioned errors related to Yum –
- bash: yum: command not found ubuntu
- Install yum in Linux
- yum command not found RedHat
- yum command not found mac
- sudo: yum: command not found ec2
- yum command not found fedora
- yum command not found centos 7
Why am I getting the yum command not found error?
Below mentioned are the possible reasons of yum command error –
- You are trying to run the “
yum” command in Debian based Linux like Ubuntu, Lubuntu, Kubuntu or Linux Mint - You are trying to run the
yumcommand on Legacy Linux e.g. Rhel 4 - Yum Utility is not installed by default in your Linux system
- You are working on the latest Linux operating system, which uses the
dnfpackage manager by default - Issue with environment variables or operating system got corrupted.
How do I solve the yum command not found error?
To resolve the yum command not found error, you need to identify your Linux distribution and it has been forked from. For example, Ubuntu is Debian based and CentOS 8, AlmaLinux, Fedora and Rocky Linux are RedHat based distros. Keep reading the solutions to get rid of “yum” error.
Note** If you are on CentOS 8, I will suggest you migrate CentOS 8 to AlmaLinux 8.x or Rocky Linux 8.x operating system. CentOS is already declared dead.
Solution-1 Make sure you are running “.rpm” based Linux Distro not Debian based Linux
If you are trying to run the “yum install” command and you are getting an error, then check your distribution is forked from RedHat, not Debian.
For example, if you try to run the yum command on Ubuntu, it will not work and results in the “yum command not found error”. Why? Because these are Debian based Distros and uses “apt” package manager, not yum.
Now the question arises, can we install and use yum on these Debian based distros? The answer is “Yes” and “No”. You can install Yum also on Debian based OS like Ubuntu using “sudo apt install yum“.
But it doesn’t make sense when you have the apt package manager already and made especially for Ubuntu. Also yum will not be able to manage your packages like apt does.
Run the following command to check the Operating system codename and version –
$ sudo cat /etc/os-release or $ sudo lsb_release -d
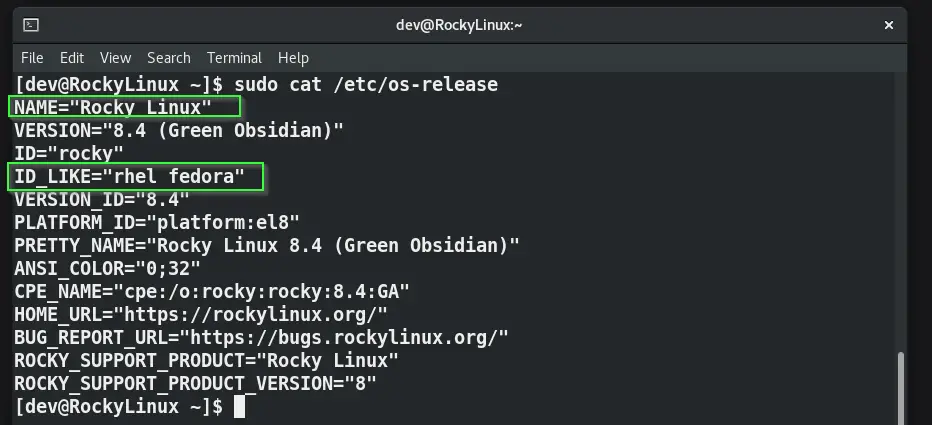
If it results in RedHat based operating systems as shown in the above image, then you are good to go with the next steps to install the Yum utility presented in Solution 2.
If any other distribution like Ubuntu, Kubuntu or Linux mint is listed. Then use the "apt" command to install packages not yum.
Refer to the following list to get a quick idea of your Linux distribution forked –
| Distribution | Forked from |
|---|---|
| AlmaLinux | Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) |
| Alpine Linux | LEAF Project |
| ALT Linux | Mandrake Linux |
| antiX | Debian, MEPIS |
| ArchBang | Arch Linux (UKM Edition) |
| Arch Linux | Independent, inspired from CRUX |
| BLAG | Fedora |
| Bodhi Linux | Debian, Ubuntu |
| Canaima | Debian, Ubuntu |
| CentOS | Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) |
| Chakra | Arch Linux[10] |
| Chrome OS | Gentoo linux |
| Clear Linux OS | Independent |
| ClearOS | RHEL, CentOS |
| CrunchBang Linux | Debian |
| Damn Small Linux | Debian, Knoppix |
| Debian | Independent, inspired by Softlanding Linux System (SLS)[17] |
| Debian Edu | Debian |
| Devuan | Debian |
| Deepin | Debian |
| Dragora GNU/Linux-Libre | Independent, inspired from Slackware |
| dyne:bolic | Debian |
| Elementary OS | Ubuntu, Debian |
| ELinOS | – |
| Emdebian Grip | Debian |
| EndeavourOS | Arch Linux |
| Fedora Linux | Red Hat Linux |
| Freespire | Ubuntu |
| Gentoo Linux | Enoch Linux |
| Guix System | – |
| gNewSense | Debian |
| Grml | Debian |
| Hyperbola GNU/Linux-libre | Arch Linux |
| Kali Linux | Debian |
| Knoppix | Debian |
| Kodibuntu | Debian, Ubuntu |
| Korora | Fedora |
| LibreCMC | Merged from LibreWRT |
| Linspire | Ubuntu |
| Linux Mint | Debian(LMDE), Ubuntu (main editions) |
| Linux Lite | Ubuntu |
| Mageia | Mandriva Linux |
| Mandriva Linux | Red Hat Linux |
| Manjaro Linux | Arch Linux |
| MEPIS | Debian |
| MIRACLE LINUX | Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) |
| Musix GNU+Linux | Debian |
| Netrunner | Debian |
| NixOS | – |
| Novell Open Enterprise Server | SUSE Linux Enterprise Server |
| OpenELEC | Kodi |
| openSUSE | SLS/Slackware |
| OpenWrt | – |
| OpenMandriva Lx | Mandriva Linux |
| Oracle Linux | Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) |
| Parabola GNU/Linux-libre | Arch Linux |
| Pardus | Gentoo (2011.2) |
| Debian | |
| Parrot OS | Debian |
| Parsix | Debian |
| Parted Magic | – |
| PCLinuxOS | Mandriva Linux |
| Pop! OS | Ubuntu |
| Pentoo | Gentoo Linux |
| Porteus | Slackware |
| Puppy Linux | Independent, inspired from Vector linux |
| PureOS | Debian |
| Qubes OS | Xen and Fedora |
| Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) | Red Hat Linux, Fedora |
| Red Hat Linux | – |
| Rocks Cluster Distribution | Red Hat Linux |
| Rocky Linux | Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) |
| ROSA | Mandriva |
| Sabayon Linux | Gentoo Linux |
| Salix OS | Slackware |
| Scientific Linux | Red Hat Linux, Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) |
| Slackware | Softlanding Linux System (SLS) |
| Slax | Debian, Slackware (until Slax 9) |
| SliTaz GNU/Linux | Independent |
| Solus | – |
| SolydXK | Debian |
| SparkyLinux | Debian |
| Source Mage GNU/Linux | Sorcerer |
| SteamOS | Debian (2.0) |
| Arch Linux (3.0) | |
| SUSE Linux Enterprise | Slackware, Jurix |
| Tails | Debian |
| Tiny Core Linux | Independent, inspired by Damn Small Linux |
| Trisquel GNU/Linux | Ubuntu LTS |
| TurnKey GNU/Linux | Debian |
| Ubuntu and Derivatives[77] | Debian |
| Univention Corporate Server | Debian |
| Ututo | Ututo XS: Gentoo Linux, Ututo UL: Ubuntu |
| VectorLinux | Slackware |
| Void Linux | Independent, partially inspired by FreeBSD/NetBSD |
| Webconverger | Debian |
| Xandros | Corel Linux |
| Zentyal | Debian, Ubuntu |
| Zenwalk | Slackware |
| Zorin OS | Ubuntu |
Solution-2 Install the yum utility, if not installed already in your Linux system
Once you have checked that you are running, RedHat based operating system like Fedora, CentOS, AlmaLinux or Rocky Linux with commands provided in Solution-1. You are good to proceed with the next steps.
If you have the right Linux distro and still you are getting the yum command not found error. Then you can install the yum utility with the following steps.
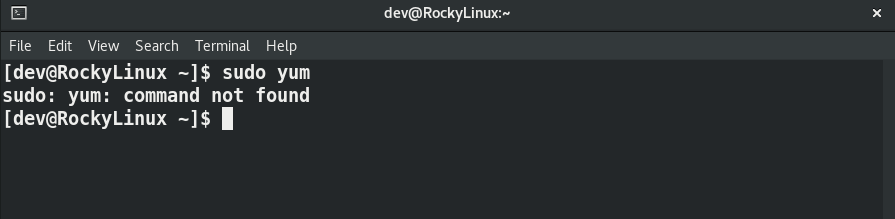
- Check whether yum package is installed or not
$ sudo yum -bash: yum: command not found
$ sudo rpm -q yum package yum is not installed or # rpm -q yum
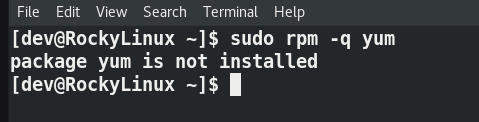
If you get “package yum is not installed” or you have wiped out the yum package by mistake, then install yum using the iso or CD/DVD.
- Mount the iso image or use the DVD of your Linux operating system and install the Yum RPM.
$ sudo rpm -ivh /path/to/yum-X.X.X-version.rpm
If you have the latest “.RPM” based Linux distro, you can use dnf also to install the yum utility.
$ sudo dnf -y install yum or # dnf -y install yum
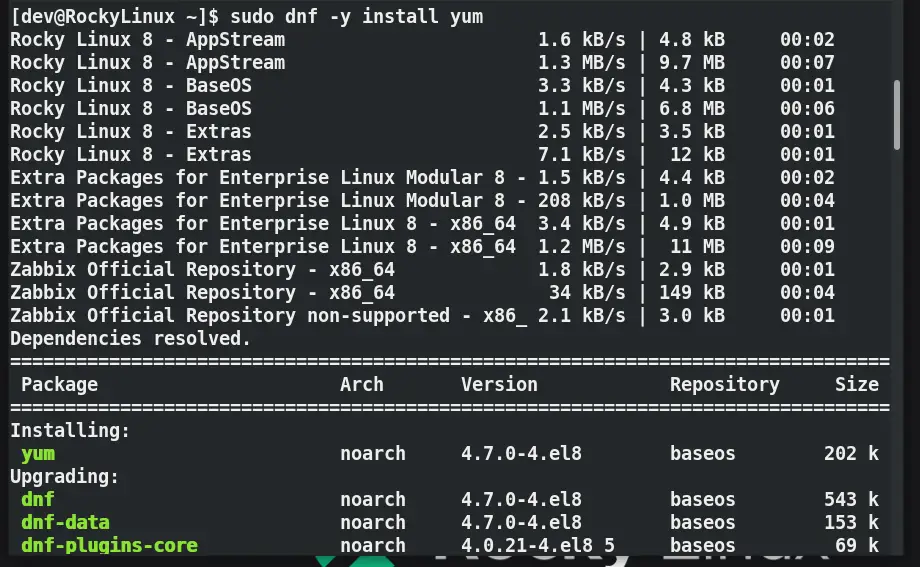
Solution-3 Avoid using legacy or out of support operating systems
I would recommend you avoid using legacy operating systems, which are already End of life (EOL) for example RedHat Linux 3, RHEL 4 etc. To check the End of life of any Linux distribution, you can visit the respected OS site and get the details.
I am recommending this because the End of Life Linux distribution repository is not updated and sometimes, you won’t be able to get the latest packages or software for your Linux operating system.
If you will use the latest RedHat forked operating systems, then you will never get an error of yum command not found as it will be available by default. Also, you can easily install it using RPMs if required.
Solution-4 Use “dnf” package manager instead of yum
DNF or Dandified YUM is the next-generation version of the Yellowdog Updater, Modified (yum), a package manager for .rpm-based distributions. Starting from RedHat 8 and Fedora 22, It has been the default package manager currently for ec2 instances also.
So if you get an error of “yum command not found“. Then use dnf instead of yum to install packages in your Linux system.
$ sudo dnf -y install yum
Solution-5 Check for $PATH is setup correctly
If you have done everything correct and you are still getting “yum command not found error” in Linux, then give a check to your $PATH entries.
Run following command make sure you have at least these entries as shown in output for root user.
# echo $PATH /usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin
If these entries are not there by default, make sure you edit and add these entries to either /etc/environment file or add it end of the ~/.bashrc file of root user.
# PATH="/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin" # export PATH
Frequently Asked questions – Yum
Q1 – How do I resolve the yum command not found?
First, check your distro name and version, it must be rpm based distro like Fedora, RedHat, Rocky Linux etc. Then look for the yum package. If it’s not installed, run “sudo dnf install yum” in case of latest Operating system. If you are using legacy OS, then install it from an iso image or CD/DVD using the “rpm -ivh /path to yum package” command.
Q2 – How do I get yum on Linux?
Run the following commands based on your distro-
– CentOS, AlmaLinux, RedHat, RockyLinux
$ sudo dnf install -y yum
– Ubuntu (use “apt” but due to some exceptions, if you need to install yum, then run”
$ sudo apt install yum
Q3 – How do I know yum is installed?
Run the following command –
$ sudo rpm -qa | grep -i yum
or
$ sudo rpm -q yum
Q4 – What is the command to install yum in Linux?
Following are the commands to install yum in Linux –
– CentOS, AlmaLinux, RedHat, RockyLinux
$ sudo dnf install -y yum
– Ubuntu (use “apt” but due to some exceptions, if you need to install yum, then run”
$ sudo apt install yum
Conclusion
I am sure you would have now resolved the “yum command not found” error by following this tutorial. If nothing is working, you may have corrupt operating system. Just reinstall your operating system, in case you are not able to run any command on your Linux operating system.


![How to fix “sudo command not found error” with examples [Update 2023]](https://cloudlinuxtech.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/12/Fix-sudo-command-not-found-error-270x161.png)
